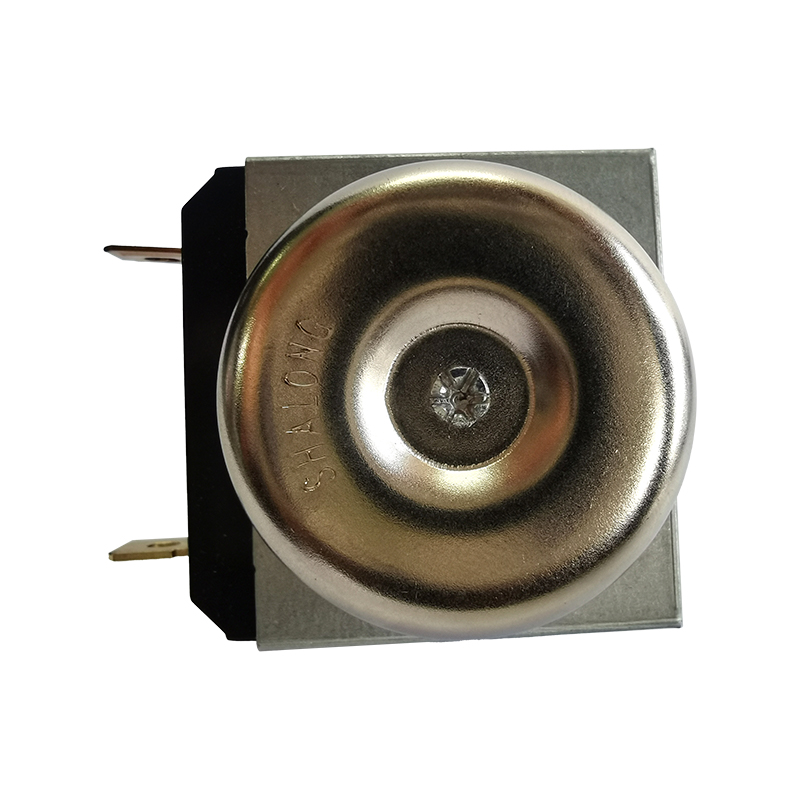
Mechanical and digital timers differ significantly in several aspects, primarily in their operating principles, accuracy, operation, applicable scenarios, and maintenance requirements.
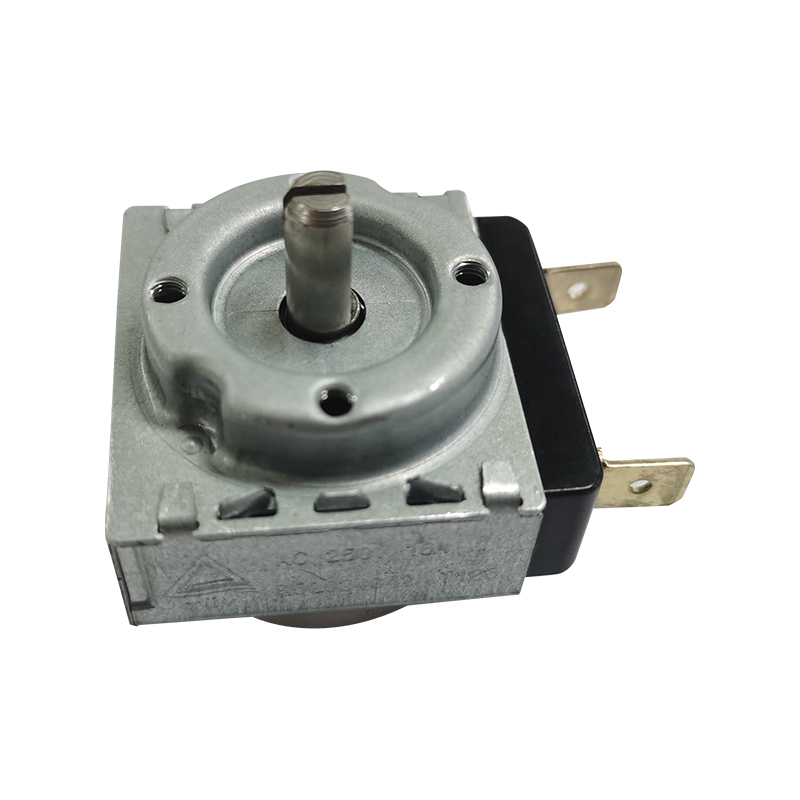
How it works: Mechanical timers rely on mechanical components (such as gears, springs, and rotating knobs) to measure time, while digital timers use electronic components (such as quartz crystal oscillators and microprocessors) to keep time. Mechanical timers use a manual switch to control the timer on/off and lack a digital display. Digital timers, on the other hand, typically use buttons and LCD or LED displays to set precise time intervals.

Accuracy: Digital timers generally have higher accuracy than mechanical timers. While the accuracy of mechanical timers is significantly affected by mechanical wear and ambient temperature, digital timers offer more precise timing due to the stability of their electronic components. For example, digital timers can have a minimum count of 0.01 seconds, while mechanical timers have a minimum count of 0.1 seconds.
Operation: Mechanical timers are relatively simple to operate; users simply rotate the hands to the desired time and press the start/stop button. Digital timers, on the other hand, can be more complex to operate, requiring settings via buttons and a display. Additionally, digital timers support programmable functions, allowing for multiple preset time periods and scheduling them weeks or months in advance.
Suitable Applications: Mechanical timers are suitable for simple tasks, such as turning lights on and off, while digital timers are suitable for complex tasks requiring precise timing, such as science experiments or cooking. Mechanical timers are bulky, consisting of large metal boxes that may not blend in with home decor; digital timers, on the other hand, are smaller, more visually appealing, and often complement a more refined design.

Maintenance Requirements: Mechanical timers' parts wear out over time, requiring regular maintenance to ensure accuracy and reliability. Digital timers, however, are electronic in nature, requiring less maintenance and less susceptible to environmental factors. Furthermore, mechanical timers require no electricity, making them suitable for locations without power outlets, while digital timers require electricity or batteries.
Cost and Reliability: Mechanical timers are relatively inexpensive and suitable for budget-conscious individuals, but they may sacrifice accuracy and convenience. Digital timers are more expensive, but offer greater accuracy and a wider range of features. Mechanical timers offer a simpler construction, increased durability, and lower maintenance costs, while digital timers' reliability may be affected by environmental factors.
Mechanical and digital timers each have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on specific application requirements, budget, design preferences, and other factors. For simple tasks, mechanical timers are a good choice; for complex tasks requiring precise timing, digital timers are more suitable.
How to Choose the Right Oven Mechanical Timer?
An Oven Mechanical Timer is a device used to control the oven's heating time. It allows the user to set a specific cooking or baking time and then issues a reminder or automatically shuts off the oven when the set time is reached. This type of timer is very common in modern ovens, not only improving cooking convenience but also enhancing cooking precision, ensuring food is cooked within the appropriate timeframe and avoiding overcooking or burning.
Choosing the right Oven Mechanical Timer requires considering several factors, including the intended use, accuracy requirements, energy consumption, and compliance with relevant safety standards. Here are a few key points:

Use: If you need precise control over baking times, choose a high-quality electronic timer. If you only need a simple timer at home, choose an affordable mechanical timer.
Accuracy Requirement: Electric timers are generally more accurate than wind-up timers, which can have some timing errors.
Energy consumption: When choosing a timer, consider its energy efficiency to ensure energy savings over extended use.
Safety standards: A qualified Oven Mechanical Timer must be of good quality and comply with relevant safety standards, such as UL and CE.
Time range: Choose the appropriate time range based on your needs. For example, some timers offer settings from 0 to 60 minutes, while others can go from 0 to 120 minutes or even longer.
Additional features: Some advanced timers may have additional features, such as alarms and multiple time settings, which can be customized based on personal preference.
Durability: High-quality mechanical timers typically have a long lifespan, such as over 100,000 cycles.
Customization options: Many manufacturers offer customization services, allowing us to adjust parameters such as time range, operating angle, and operating torque to meet customer requirements.
By considering these factors, you can choose the Oven Mechanical Timer that best suits your needs.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体